Overpronation Of The Feet Discomfort
Pronation is a turning outward of the foot at the ankle, which allows the foot to flatten. The pronation helps to absorb some of the compressive shock forces, torque conversion, adjustment to uneven ground contours, and maintenance of balance. It is necessary to have a certain amount of pronation to disseminate the energy of the foot-strike. If there is too little or too much pronation injuries may occur. When a foot and ankle pronates to a great degree, we call it over-pronation. Normally you can see the Achilles Tendon run straight down the leg into the heel. If the foot is over-pronated, the tendon will run straight down the leg, but when it lies on the heel it will twist outward. This makes the inner ankle bone much more prominent than the outer ankle bone.
Causes
Generally fallen arches are a condition inherited from one or both parents. In addition, age, obesity, and pregnancy cause our arches to collapse. Being in a job that requires long hours of standing and/or walking (e.g. teaching, retail, hospitality, building etc) contributes to this condition, especially when standing on hard surfaces like concrete floors. Last, but not least unsupportive footwear makes our feet roll in more than they should.
Symptoms
Over-pronation is a condition where the arch flattens out which makes the feet roll inward while walking. This condition is also known as flat feet. It imposes extreme additional stresses on the plantar fascia, a fibrous band of tissue which connects the heel to the forefoot. Over-pronation makes walking a painful experience because of the additional strain on the calves, heel and/or back. Treatment for over-pronation involves the use of specially-made orthotics which offers arch support and medial rear foot posting as corrective measures.
Diagnosis
Bunions, calluses and crooked toes may indicate alignment problems. So, it is important to ascertain the condition of a client's toes. Check the big toe to determine if the first joint of the toe is swollen, has a callus or bunion, and/or looks as though it abducts (i.e., hallux valgus) rather than pointing straight ahead. Also, look to see if the lesser toes seem to "curl up" (i.e., the person has hammer or claw toes). This may be indicative of damage to, or inflexibility of the plantar fascia caused by excessive flattening of the foot.
Non Surgical Treatment
Pronation and supination are bio-mechanical problems, and are best treated and prevented with orthotic inserts. But before you run out to buy orthotics it makes sense to get the right advice on footwear, and the best advice I can give you, is to go and see a qualified podiatrist for a complete foot-strike and running gait analysis. They will be able to tell you if there are any concerns regarding the way your running gait is functioning. After your running gait has been analysed, have your podiatrist, or competent sports footwear sales person recommend a number of shoes that suit your requirements. Good quality footwear will go a long way in helping to prevent pronation and supination. And, if needed, invest in a pair of orthotic inserts to further prevent excessive pronation or supination.
Prevention
Many of the prevention methods for overpronation orthotics, for example, can be used interchangeably with treatment methods. If the overpronation is severe, you should seek medical attention from a podiatrist who can cast you for custom-made orthotics. Custom-made orthotics are more expensive, but they last longer and provide support, stability, and balance for the entire foot. You can also talk with a shoe specialist about running shoes that offer extra medial support and firm heel counters. Proper shoes can improve symptoms quickly and prevent them from recurring. Surgery can sometimes help cure and prevent this problem if you suffer from inherited or acquired pes planus deformity. Surgery typically involves stabilizing the bones to improve the foot?s support and function.
Physiotherapy For Severs Disease
Sever's disease or Calcaneal apophysitis is a condition that affects children between the ages of 10 and 13 years. It is characterized by pain in one or both heels with walking. During this phase of life, growth of the bone is taking place at a faster rate than the tendons. Hence there is a relative shortening of the heel-cord compared to the leg bones. As a result, the tension the heel-cord applies to the heel bone at its insertion is very great. Moreover, the heel cord is attached to a portion of the calcaneus (heel bone) that is still immature, consisting of a mixture of bone and growing cartilage, called the calcaneal apophysis, which is prone to injury. Compounding to this is the fact that all these changes are happening in a very active child, prone to overuse. The end result is therefore an overuse syndrome of injury and inflammation at the heel where the heel cord (Achilles Tendonitis) inserts into the heel bone (Calcaneal apophysitis).
Causes
The actual pathology of the condition is one of more of an overuse syndrome in which the growth plate of the heel may become slightly displaced, causing pain. Biopsies of similar conditions have shown changes consistent with separation of the cartilage. The cause of Sever's disease is not entirely clear. It is most likely due to overuse or repeated minor trauma that happens in a lot of sporting activities - the cartilage join between the two parts of the bone can not take all the shear stress of the activities. Some children seem to be just more prone to it for an unknown reason, combine this with sport, especially if its on a hard surface and the risk of getting it increases. A pronated foot and tight calf muscles are common contributing factors. The condition is very similar to Osgood-Schlatters Disease which occurs at the knee.
Symptoms
The main symptom of sever's disease is pain and tenderness at the back of the heel which is made worse with physical activity. Tenderness will be felt especially if you press in or give the back of the heel a squeeze from the sides. There may be a lump over the painful area. Another sign is tight calf muscles resulting with reduced range of motion at the ankle. Pain may go away after a period of rest from sporting activities only to return when the young person goes back to training.
Diagnosis
Sever's disease is diagnosed based on a doctor?s physical examination of the lower leg, ankle, and foot. If the diagnosis is in question, the doctor may order X-rays or an MRI to determine if there are other injuries that may be causing the heel pain.
Non Surgical Treatment
First, your child should cut down or stop any activity that causes heel pain. Apply ice to the injured heel for 20 minutes 3 times a day. If your child has a high arch, flat feet or bowed legs, your doctor may recommend orthotics, arch supports or heel cups. Your child should never go barefoot. If your child has severe heel pain, medicines such as acetaminophen (one brand name: Tylenol) or ibuprofen (some brand names. Advil, Motrin, Nuprin) may help.
Recovery
In some cases, children will simply outgrow Sever's Disease when they reach a certain age, but this does not mean that symptoms should be ignored. If children express that they are in pain, this should always be taken seriously by their parents or guardians. Heel pain may be a sign of Sever's Disease and this condition should not be left untreated, due to the damage it can cause to the growing heel bones. Scheduling a doctor's appointment is always the first step to take in gaining a diagnosis of symptoms and speedy help for the child.
Acquired Flat Foot Tibialis Posterior Muscle
Overview
Adult acquired flatfoot deformity (AAFD), embraces a wide spectrum of deformities. AAFD is a complex pathology consisting both of posterior tibial tendon insufficiency and failure of the capsular and ligamentous structures of the foot. Each patient presents with characteristic deformities across the involved joints, requiring individualized treatment. Early stages may respond well to aggressive conservative management, yet more severe AAFD necessitates prompt surgical therapy to halt the progression of the disease to stages requiring more complex procedures. We present the most current diagnostic and therapeutic approaches to AAFD, based on the most pertinent literature and our own experience and investigations. 
Causes
There are numerous causes of acquired adult flatfoot, including fracture or dislocation, tendon laceration, tarsal coalition, arthritis, neuroarthropathy, neurologic weakness, and iatrogenic causes. The most common cause of acquired adult flatfoot is posterior tibial tendon dysfunction.
Symptoms
As different types of flatfoot have different causes, the associated symptoms can be different for different people. Some generalized symptoms are listed. Pain along the course of the posterior tibial tendon which lies on the inside of the foot and ankle. This can be associated with swelling on the inside of the ankle. Pain that is worse with activity. High intensity or impact activities, such as running and jumping, can be very difficult. Some patients can have difficulty walking or even standing for long periods of time and may experience pain at the inside of the ankle and in the arch of the foot. Feeling like one is ?dragging their foot.? When the foot collapses, the heel bone may shift position and put pressure on the outside ankle bone (fibula). This can cause pain in the bones and tendons in the outside of the ankle joint. Patients with an old injury or arthritis in the middle of the foot can have painful, bony bumps on the top and inside of the foot. These make shoe wear very difficult. Sometimes, the bony spurs are so large that they pinch the nerves which can result in numbness and tingling on the top of the foot and into the toes. Diabetic patients may not experience pain if they have damage to their nerves. They may only notice swelling or a large bump on the bottom of the foot. The large bump can cause skin problems and an ulcer (a sore that does not heal) may develop if proper diabetic shoe wear is not used.
Diagnosis
There are four stages of adult-acquired flatfoot deformity (AAFD). The severity of the deformity determines your stage. For example, Stage I means there is a flatfoot position but without deformity. Pain and swelling from tendinitis is common in this stage. Stage II there is a change in the foot alignment. This means a deformity is starting to develop. The physician can still move the bones back into place manually (passively). Stage III adult-acquired flatfoot deformity (AAFD) tells us there is a fixed deformity. This means the ankle is stiff or rigid and doesn???t move beyond a neutral (midline) position. Stage IV is characterized by deformity in the foot and the ankle. The deformity may be flexible or fixed. The joints often show signs of degenerative joint disease (arthritis).
Non surgical Treatment
Initial treatment is based on the degree of deformity and flexibility at initial presentation. Conservative treatment includes orthotics or ankle foot orthoses (AFO) to support the posterior tibial tendon (PT) and the longitudinal arch, anti-inflammatories to help reduce pain and inflammation, activity modification which may include immobilization of the foot and physical therapy to help strengthen and rehabilitate the tendon. 
Surgical Treatment
Surgical intervention for adult acquired flatfoot is appropriate when there is pain and swelling, and the patient notices that one foot looks different than the other because the arch is collapsing. As many as three in four adults with flat feet eventually need surgery, and it?s better to have the joint preservation procedure done before your arch totally collapses. In most cases, early and appropriate surgical treatment is successful in stabilizing the condition.
Adult Aquired Flat Feet Do I Suffer AAF?
Another common term for this condition is Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction (PTTD). There is a cause-effect relationship between pronation, flatfoot deformity and subsequent tenosynovitis of the posterior tibial tendon. Mechanical irritation of the tendon may lead to synovitis, partial tearing and eventually full rupture of the tendon. Other structures, including ligaments and the plantar fascia, have also been shown to contribute to the arch collapsing. As the deformity progresses, these structures have been shown to attenuate and rupture as well. In later stages, subluxation of various joints lead to a valgus rearfoot and transverse plane deformity of the forefoot. These deformities can become fixed and irreducible as significant osteoarthritis sets in.
Causes
A person with flat feet has greater load placed on the posterior tibial tendon which is the main tendon unit supporting up the arch of the foot. Throughout life, aging leads to decreased strength of muscles, tendons and ligaments. The blood supply diminishes to tendons with aging as arteries narrow. Heavier, obese patients have more weight on the arch and have greater narrowing of arteries due to atherosclerosis. In some people, the posterior tibial tendon finally gives out or tears. This is not a sudden event in most cases. Rather, it is a slow, gradual stretching followed by inflammation and degeneration of the tendon. Once the posterior tibial tendon stretches, the ligaments of the arch stretch and tear. The bones of the arch then move out of position with body weight pressing down from above. The foot rotates inward at the ankle in a movement called pronation. The arch appears collapsed, and the heel bone is tilted to the inside. The deformity can progress until the foot literally dislocates outward from under the ankle joint.
Symptoms
The first stage represents inflammation and symptoms originating from an irritated posterior tibial tendon, which is still functional. Stage two is characterized by a change in the alignment of the foot noted on observation while standing (see above photos). The deformity is supple meaning the foot is freely movable and a ?normal? position can be restored by the examiner. Stage two is also associated with the inability to perform a single-leg heel rise. The third stage is dysfunction of the posterior tibial tendon is a flatfoot deformity that becomes stiff because of arthritis. Prolonged deformity causes irritation to the involved joints resulting in arthritis. The fourth phase is a flatfoot deformity either supple (stage two) or stiff (stage 3) with involvement of the ankle joint. This occurs when the deltoid ligament, the major supporting structure on the inside of the ankle, fails to provide support. The ankle becomes unstable and will demonstrate a tilted appearance on X-ray. Failure of the deltoid ligament results from an inward displacement of the weight bearing forces. When prolonged, this change can lead to ankle arthritis. The vast majority of patients with acquired adult flatfoot deformity are stage 2 by the time they seek treatment from a physician.
Diagnosis
Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction is diagnosed with careful clinical observation of the patient?s gait (walking), range of motion testing for the foot and ankle joints, and diagnostic imaging. People with flatfoot deformity walk with the heel angled outward, also called over-pronation. Although it is normal for the arch to impact the ground for shock absorption, people with PTTD have an arch that fully collapses to the ground and does not reform an arch during the entire gait period. After evaluating the ambulation pattern, the foot and ankle range of motion should be tested. Usually the affected foot will have decreased motion to the ankle joint and the hindfoot. Muscle strength may also be weaker as well. An easy test to perform for PTTD is the single heel raise where the patient is asked to raise up on the ball of his or her effected foot. A normal foot type can lift up on the toes without pain and the heel will invert slightly once the person has fully raised the heel up during the test. In early phases of PTTD the patient may be able to lift up the heel but the heel will not invert. An elongated or torn posterior tibial tendon, which is a mid to late finding of PTTD, will prohibit the patient from fully rising up on the heel and will cause intense pain to the arch. Finally diagnostic imaging, although used alone cannot diagnose PTTD, can provide additional information for an accurate diagnosis of flatfoot deformity. Xrays of the foot can show the practitioner important angular relationships of the hindfoot and forefoot which help diagnose flatfoot deformity. Most of the time, an MRI is not needed to diagnose PTTD but is a tool that should be considered in advanced cases of flatfoot deformity. If a partial tear of the posterior tibial tendon is of concern, then an MRI can show the anatomic location of the tear and the extensiveness of the injury.
Non surgical Treatment
Treatment will vary depending on the degree of your symptoms. Generally, we would use a combination of rest, immobilization, orthotics, braces, and physical therapy to start. The goal is to keep swelling and inflammation under control and limit the stress on the tendon while it heals. Avoidance of activities that stress the tendon will be necessary. Once the tendon heals and you resume activity, physical therapy will further strengthen the injured tendon and help restore flexibility. Surgery may be necessary if the tendon is torn or does not respond to these conservative treatment methods. Your posterior tibial tendon is vital for normal walking. When it is injured in any way, you risk losing independence and mobility. Keep your foot health a top priority and address any pain or problems quickly. Even minor symptoms could progress into chronic problems, so don?t ignore your foot pain.

Surgical Treatment
In cases where cast immobilization, orthoses and shoe therapy have failed, surgery is the next alternative. The goal of surgery and non-surgical treatment is to eliminate pain, stop progression of the deformity and improve mobility of the patient. Opinions vary as to the best surgical treatment for adult acquired flatfoot. Procedures commonly used to correct the condition include tendon debridement, tendon transfers, osteotomies (cutting and repositioning of bone) and joint fusions. (See surgical correction of adult acquired flatfoot). Patients with adult acquired flatfoot are advised to discuss thoroughly the benefits vs. risks of all surgical options. Most procedures have long-term recovery mandating that the correct procedure be utilized to give the best long-term benefit. Most flatfoot surgical procedures require six to twelve weeks of cast immobilization. Joint fusion procedures require eight weeks of non-weightbearing on the operated foot - meaning you will be on crutches for two months. The bottom line is, Make sure all of your non-surgical options have been covered before considering surgery. Your primary goals with any treatment are to eliminate pain and improve mobility. In many cases, with the properly designed foot orthosis or ankle brace, these goals can be achieved without surgical intervention.
Working with With Achilles Tendinitis Problems
 Achilles tendonitis is an inflammation of the Achilles tendon. This inflammation is typically short-lived. Over time, if not resolved, the condition may progress to a degeneration of the tendon (Achilles tendonosis), in which the tendon loses its organized structure and is likely to develop microscopic tears. Sometimes the degeneration involves the site where the Achilles tendon attaches to the heel bone. In rare cases, chronic degeneration with or without pain may result in rupture of the tendon.
Achilles tendonitis is an inflammation of the Achilles tendon. This inflammation is typically short-lived. Over time, if not resolved, the condition may progress to a degeneration of the tendon (Achilles tendonosis), in which the tendon loses its organized structure and is likely to develop microscopic tears. Sometimes the degeneration involves the site where the Achilles tendon attaches to the heel bone. In rare cases, chronic degeneration with or without pain may result in rupture of the tendon.
Causes
As ?overuse? disorders, Achilles tendonitis and tendonosis are usually caused by a sudden increase of a repetitive activity involving the Achilles tendon. Such activity puts too much stress on the tendon too quickly, leading to micro-injury of the tendon fibers. Due to this ongoing stress on the tendon, the body is unable to repair the injured tissue. The structure of the tendon is then altered, resulting in continued pain. Achilles4Athletes are at high risk for developing disorders of the Achilles tendon. Achilles tendonitis and tendonosis are also common in individuals whose work puts stress on their ankles and feet, such as laborers, as well as in ?weekend warriors?-those who are less conditioned and participate in athletics only on weekends or infrequently. In addition, people with excessive pronation (flattening of the arch) have a tendency to develop Achilles tendonitis and tendonosis due to the greater demands placed on the tendon when walking. If these individuals wear shoes without adequate stability, their over-pronation could further aggravate the Achilles tendon.
Symptoms
Dull or sharp pain anywhere along the back of the tendon, but usually close to the heel. limited ankle flexibility redness or heat over the painful area a nodule (a lumpy build-up of scar tissue) that can be felt on the tendon a cracking sound (scar tissue rubbing against tendon) with ankle movement.
Diagnosis
On examination, an inflamed or partially torn Achilles tendon is tender when squeezed between the fingers. Complete tears are differentiated by sudden, severe pain and inability to walk on the extremity. A palpable defect along the course of the tendon. A positive Thompson test (while the patient lies prone on the examination table, the examiner squeezes the calf muscle; this maneuver by the examiner does not cause the normally expected plantar flexion of the foot).
Nonsurgical Treatment
The aim of the treatment is to reduce strain on the tendon and reduce inflammation. Strain may be reduced by, avoiding or severely limiting activities that may aggravate the condition, such as running, using shoe inserts (orthoses) to take pressure off the tendon as it heals. In cases of flat or hyperpronated feet, your doctor or podiatrist may recommend long-term use of orthoses. I8nflammation may be reduced by, applying icepacks for 20 minutes per hour during the acute stage, taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, placing the foot in a cast or restrictive ankle-boot to minimise movement and give the tendon time to heal. This may be recommended in severe cases and used for about eight weeks. Occasionally depot (slowly absorbed) steroid injections may be tried, particularly for peri-tendinitis, but great care needs to be taken to avoid injecting into the tendon. This should only be done by a specialist doctor. You may also be given specific exercises to gently stretch the calf muscles once the acute stage of inflammation has settled down. Your doctor or physiotherapist will recommend these exercises when you are on the road to recovery. Recovery is often slow and will depend on the severity of the condition and how carefully you follow the treatment and care instructions you are given.

Surgical Treatment
Around 1 in 4 people who have persisting pain due to Achilles tendinopathy has surgery to treat the condition. Most people have a good result from surgery and their pain is relieved. Surgery involves either of the following, removing nodules or adhesions (parts of the fibres of the tendon that have stuck together) that have developed within the damaged tendon. Making a lengthways cut in the tendon to help to stimulate and encourage tendon healing. Complications from surgery are not common but, if they do occur, can include problems with wound healing.
Prevention
To prevent Achilles tendonitis or tendonosis from recurring after surgical or non-surgical treatment, the foot and ankle surgeon may recommend strengthening and stretching of the calf muscles through daily exercises. Wearing proper shoes for the foot type and activity is also important in preventing recurrence of the condition.
What Brings About Plantar Fasciitis To Appear
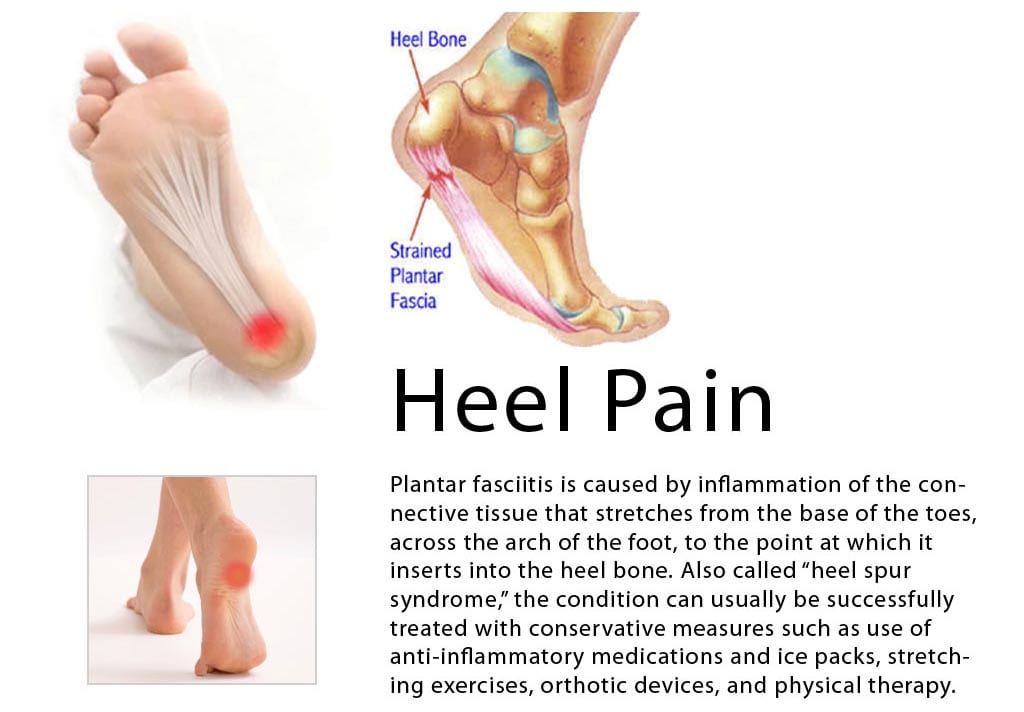
Overview
Plantar fasciitis is a poorly understood condition. There is little consensus among medical professionals about what causes the problem, and no treatments have been reliably proven to treat it. A number of theories exists for why plantar fasciitis develops, but the ineffectiveness of conventional treatments suggests something is missing. The plantar fascia is a band of connective tissue that runs along the underside of the foot from the heel to the toes. The fascia helps maintain the integrity of the arch, provides shock absorption, and plays an important role in the normal mechanical function of the foot.
Causes
The cause of plantar fasciitis is often unclear and may be multifactorial. Because of the high incidence in runners, it is best postulated to be caused by repetitive microtrauma. Possible risk factors include obesity, occupations requiring prolonged standing and weight-bearing, and heel spurs. Other risk factors may be broadly classified as either extrinsic (training errors and equipment) or intrinsic (functional, structural, or degenerative). Training errors are among the major causes of plantar fasciitis. Athletes usually have a history of an increase in distance, intensity, or duration of activity. The addition of speed workouts, plyometrics, and hill workouts are particularly high-risk behaviors for the development of plantar fasciitis. Running indoors on poorly cushioned surfaces is also a risk factor. Appropriate equipment is important. Athletes and others who spend prolonged time on their feet should wear an appropriate shoe type for their foot type and activity. Athletic shoes rapidly lose cushioning properties. Athletes who use shoe-sole repair materials are especially at risk if they do not change shoes often. Athletes who train in lightweight and minimally cushioned shoes (instead of heavier training flats) are also at higher risk of developing plantar fasciitis.
Symptoms
Plantar fasciitis and heel spur pain usually begins in the bottom of the heel, and frequently radiates into the arch. At times, however, the pain may be felt only in the arch. The pain is most intense when first standing, after any period of rest. Most people with this problem experience their greatest pain in the morning, with the first few steps after sleeping. After several minutes of walking, the pain usually becomes less intense and may disappear completely, only to return later with prolonged walking or standing. If a nerve is irritated due to the swollen plantar fascia, this pain may radiate into the ankle. In the early stages of Plantar Fasciitis and Heel Spurs, the pain will usually subside quickly with getting off of the foot and resting. As the disease progresses, it may take longer periods of time for the pain to subside.
Diagnosis
To arrive at a diagnosis, the foot and ankle surgeon will obtain your medical history and examine your foot. Throughout this process the surgeon rules out all the possible causes for your heel pain other than plantar fasciitis. In addition, diagnostic imaging studies such as x-rays or other imaging modalities may be used to distinguish the different types of heel pain. Sometimes heel spurs are found in patients with plantar fasciitis, but these are rarely a source of pain. When they are present, the condition may be diagnosed as plantar fasciitis/heel spur syndrome.
Non Surgical Treatment
Management options are usually conservative. Local injection of steroids, local anaesthetic may be useful to manage symptoms. Ultrasound-guided steroid injection has been shown to be effective in short-term (four-week) pain relief and reduced thickness of the plantar fascia at three months. A posterior tibial nerve block can be performed prior for a less painful plantar fascia injection. Specific plantar fascia stretching exercises performed daily have been shown to reduce short-term (8 weeks) and long-term (two years) pain. Other supportive measures include weight reduction in obese patients, rest, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and reduction of weight-bearing pressure (soft rubber heel pad, molded orthosis, or heel cup or soft-soled shoes).
Surgical Treatment
The most dramatic therapy, used only in cases where pain is very severe, is surgery. The plantar fascia can be partially detached from the heel bone, but the arch of the foot is weakened and full function may be lost. Another surgery involves lengthening the calf muscle, a process called gastrocnemius recession. If you ignore the condition, you can develop chronic heel pain. This can change the way you walk and cause injury to your legs, knees, hips and back. Steroid injections and some other treatments can weaken the plantar fascia ligament and cause potential rupture of the ligament. Surgery carries the risks of bleeding, infection, and reactions to anesthesia. Plantar fascia detachment can also cause changes in your foot and nerve damage. Gastrocnemius resection can also cause nerve damage.
What Brings About Heel Discomfort And Approaches To Overcome It
Overview
There are many diagnoses within the differential of heel pain; however, plantar fasciitis is the most common cause of heel pain for which professional care is sought. Approximately 10% of the United States population experiences bouts of heel pain, which results in 1 million visits per year to medical professionals for treatment of plantar fasciitis. The annual cost of treatments for plantar fasciitis is estimated to be between $192 and $376 million dollars. The etiology of this condition is multifactorial, and the condition can occur traumatically; however, most cases are from overuse stresses.
Causes
Patients with tight calf muscles will suffer with excessive pulling of the muscle group on the back of the heel. This in turn creates pulling of other structures that are attached to the heel, including the Plantar Fascia. When the pulling continues for long enough, then inflammation will develop and lead to Plantar Fasciitis. This causes Heel Pain. It is extremely common for patients who increase their level of activity to develop Plantar Fasciitis. Boot camp, running, zumba, recreational walking or other quick movement sports such as tennis or touch football are typical causes of Heel Pain. The sharp increase in exercise is too much for the foot to cope with and the stress on the Plantar Fascia causes inflammation. The Heel Pain that is caused by this inflammation is known as Plantar Fasciitis.
Symptoms
Symptoms of plantar fasciitis include pain in the heel of the foot. Some people complain of a sharp stabbing pain especially with walking. Others describe the pain as a dull ache after prolonged standing. The pain of plantar fasciitis is often worst in the morning or following activity.
Diagnosis
Plantar fasciitis is usually diagnosed by your physiotherapist or sports doctor based on your symptoms, history and clinical examination. After confirming your plantar fasciitis they will investigate WHY you are likely to be predisposed to plantar fasciitis and develop a treatment plan to decrease your chance of future bouts. X-rays may show calcification within the plantar fascia or at its insertion into the calcaneus, which is known as a calcaneal or heel spur. Ultrasound scans and MRI are used to identify any plantar fasciitis tears, inflammation or calcification. Pathology tests (including screening for HLA B27 antigen) may identify spondyloarthritis, which can cause symptoms similar to plantar fasciitis.
Non Surgical Treatment
Sometimes physical therapy modalities are helpful. The most frequently used modalities include ultrasound (high frequency sound vibrations that create a deep heat and reduce inflammation) and galvanic electrical stimulation ( a carefully applied intermittent muscular stimulation to the heel and calf that helps reduce pain and relax muscle spasm, which is a contributing factor to the pain). This treatment has been found most effective when given twice a week. Repeated taping and padding is sometimes used. The felt pads that will be strapped to your feet will compress after a few days and must be reapplied. While wearing them they should be kept dry, but may be removed the night before your next appointment. Resistant cases of heel pain caused by plantar fasciitis, heel spurs or cases of stress fracture of the calcaneus often need to be placed in a removable below knee cast boot. It is important to be aware of how your foot feels over this time period. If your foot is still uncomfortable without the strapping, but was more comfortable while wearing it, that is an indication that the treatment should help. Remember, what took many months or years to develop can not be eliminated in just a few days.

Surgical Treatment
Surgery should be reserved for patients who have made every effort to fully participate in conservative treatments, but continue to have pain from plantar fasciitis. Patients should fit the following criteria. Symptoms for at least 9 months of treatment. Participation in daily treatments (exercises, stretches, etc.). If you fit these criteria, then surgery may be an option in the treatment of your plantar fasciitis. Unfortunately, surgery for treatment of plantar fasciitis is not as predictable as a surgeon might like. For example, surgeons can reliably predict that patients with severe knee arthritis will do well after knee replacement surgery about 95% of the time. Those are very good results. Unfortunately, the same is not true of patients with plantar fasciitis.
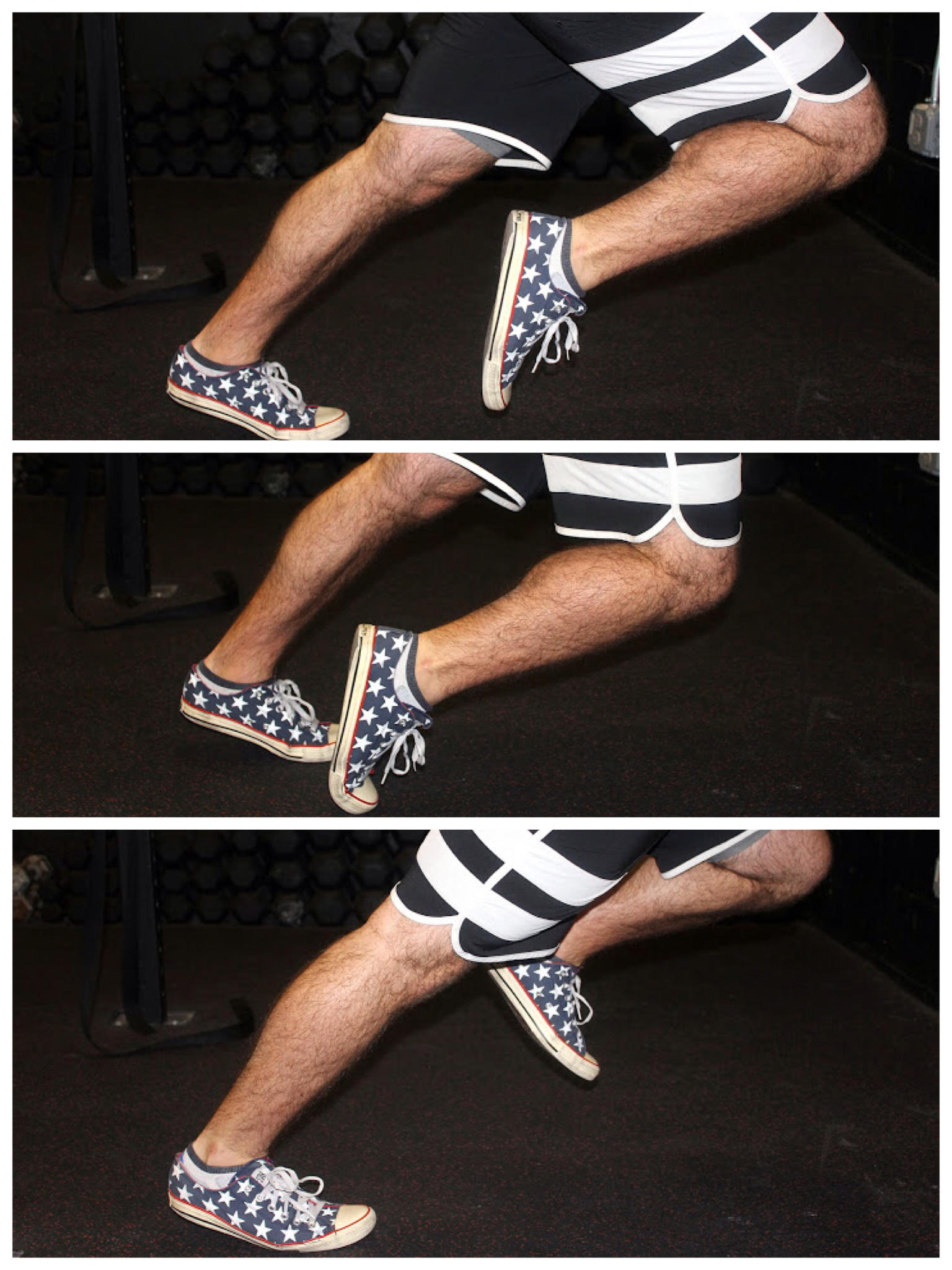
Stretching Exercises
In one exercise, you lean forward against a wall with one knee straight and heel on the ground. Your other knee is bent. Your heel cord and foot arch stretch as you lean. Hold for 10 seconds, relax and straighten up. Repeat 20 times for each sore heel. It is important to keep the knee fully extended on the side being stretched. In another exercise, you lean forward onto a countertop, spreading your feet apart with one foot in front of the other. Flex your knees and squat down, keeping your heels on the ground as long as possible. Your heel cords and foot arches will stretch as the heels come up in the stretch. Hold for 10 seconds, relax and straighten up. Repeat 20 times. About 90 percent of people with plantar fasciitis improve significantly after two months of initial treatment. You may be advised to use shoes with shock-absorbing soles or fitted with an off-the-shelf shoe insert device like a rubber heel pad. Your foot may be taped into a specific position. If your plantar fasciitis continues after a few months of conservative treatment, your doctor may inject your heel with steroidal anti-inflammatory medication. If you still have symptoms, you may need to wear a walking cast for two to three weeks or a positional splint when you sleep. In a few cases, surgery is needed for chronically contracted tissue.