The Right Way To Identify Posterior Calcaneal Spur
Overview
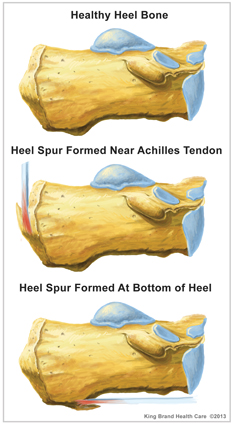
Heel spurs are a common foot problem resulting from excess bone growth on the heel bone. The bone growth is usually located on the underside of the heel bone, extending forward to the toes. One explanation for this excess production of bone is a painful tearing of the plantar fascia connected between the toes and heel. This can result in either a heel spur or an inflammation of the plantar fascia, medically termed plantar fascitis. Because this condition is often correlated to a decrease in the arch of the foot, it is more prevalent after the age of six to eight years, when the arch is fully developed.
Causes
Heel spurs can form as a result of repeated strain placed on foot muscles and ligaments as well as from abnormally stretching the band of tissue connecting the heel and ball of the foot. Repeated injury to the membrane that lines the heel bone can also cause problems as can repeated tight pressure on the back of the heel. The causes can range from excessive walking (especially if unaccustomed to walking), running or jumping to improperly fitted or worn-out shoes. Runners, volleyball players, and tennis players, people who do step aerobics or stair climbing for exercise, those with flat feet, pregnant women, the obese and diabetics and those who wear tight-fitting shoes with a high heel are all prone to developing spurs (and plantar fasciitis) more readily.
Symptoms
Some symptoms at the beginning of this condition include pain and swelling, and discomfort when pushing off with the toes during walking. This movement of the foot stretches the fascia that is already irritated and inflamed. If this condition is not treated, pain will be noticed in the heel when a heel spur develops in response to the stress. This is a common condition among athletes and others who run and jump a significant amount.
Diagnosis
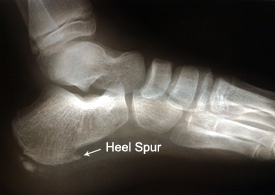
Heel spurs and plantar fasciitis are diagnosed based on the history of pain and tenderness localized to these areas. They are specifically identified when there is point tenderness at the bottom of the heel, which makes it difficult to walk barefoot on tile or wood floors. X-ray examination of the foot is used to identify the bony prominence (spur) of the heel bone (calcaneus).
Non Surgical Treatment
The most important part of treatment is to rest. Do not undertake activities which hurt the foot or aggravate symptoms as will only cause painful symptoms to persist. Apply an ice pack regularly for 10 minutes at a time every hour initially to reduce pain and inflammation of the surrounding tissues. As symptoms subside frequency of application can reduce to 2 or 3 times per day. Exercises and stretches to keep the foot and ankle strong and mobile are important as long as pain allows. Stretching the plantar fascia is important, especially if symptoms are worse in the morning. A plantar fasciitis night splint is excellent for stretching and preventing the plantar fascia tightening up over night. Anti-Inflammatory medicine (e.g. ibuprofen) may be prescribed by a doctor but always check with a medical professional first as taking some medications such as ibuprofen should not be done if the patient has asthma. Shoe inserts can help to take the pressure off of the spur and reduce pain. If these treatments do not significantly ease the symptoms then surgery may be an option.
Surgical Treatment
Usually, heel spurs are curable with conservative treatment. If not, heel spurs are curable with surgery, although there is the possibility of them growing back. About 10% of those who continue to see a physician for plantar fascitis have it for more than a year. If there is limited success after approximately one year of conservative treatment, patients are often advised to have surgery.
Prevention
A variety of steps can be taken to avoid heel pain and accompanying afflictions. Wear shoes that fit well-front, back, and sides-and have shock-absorbent soles, rigid shanks, and supportive heel counters. Wear the proper shoes for each activity. Do not wear shoes with excessive wear on heels or soles. Prepare properly before exercising. Warm up and do stretching exercises before and after running. Pace yourself when you participate in athletic activities. Don't underestimate your body's need for rest and good nutrition. If obese, lose weight.
How Would You Treat Bursitis Of The Foot
Retrocalcaneal bursitis most commonly occurs as s result of repetitive activity that encourages the calf muscles to tighten and shorten from overuse, like repetitively wearing high heels, running and even wearing tight shoes that pinch at the back of the heel. Symptoms normally include a constant dull ache or burning pain at the back of the heel that is aggravated by any touch or pressure from tight shoes or movement of the ankle joint. There will normally be noticeable swelling around the back of the heel. In cases of bursitis caused by infection the skin around the affected joint will appear red and will feel incredibly warm to the touch. Additional symptoms are a high temperature and feverish chills. Retrocalcaneal bursitis is very similar to Achilles bursitis as the bursae are very close in proximity and symptoms are almost identical however retrocalcaneal bursitis is a lot more common.
Causes
Bursitis of the Achilles tendon is caused by the irritation and inflammation of the retrocalcaneal bursa, a small fluid-filled sac located in the back of the ankle that acts as a cushion and lubricant for the ankle joint. Possible causes of Achilles tendon bursitis include aging, Factors related to the aging process, including the onset of rheumatoid arthritis and gout, can deteriorate the bursa. Overuse of ankle. Excessive walking, uphill running, jumping, and other aggressive exercise regimens, especially without proper conditioning, can cause irritation to the bursa. Trauma. Sudden injury to the ankle joint, or trauma caused by rigid or improperly fitted shoes, can increase the chances of developing bursitis.
Symptoms
Bursitis usually causes a dull pain, tenderness, and stiffness near the affected bursa. The bursa may swell and make the skin around it red and warm to the touch. Bursitis is most common in the shoulder camera.gif, elbow camera.gif, hip camera.gif, and knee camera.gif. Bursitis may also occur near the Achilles tendon or in the foot. Symptoms of bursitis may be like those of tendinopathy. Both occur in the tissues in and around the joints. Check with your doctor if your pain is severe, if the sore area becomes very hot or red, or if you have a fever.
Diagnosis
On physical examination, patients have tenderness at the site of the inflamed bursa. If the bursa is superficial, physical examination findings are significant for localized tenderness, warmth, edema, and erythema of the skin. Reduced active range of motion with preserved passive range of motion is suggestive of bursitis, but the differential diagnosis includes tendinitis and muscle injury. A decrease in both active and passive range of motion is more suggestive of other musculoskeletal disorders. In patients with chronic bursitis, the affected limb may show disuse atrophy and weakness. Tendons may also be weakened and tender.
Non Surgical Treatment
Conservative treatment of bursitis is usually effective. The application of heat, rest, and immobilization of the affected joint area is the first step. A sling can be used for a shoulder injury, a cane is helpful for hip problems. The patient can take nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like aspirin, ibuprofin, and naproxen. They can be obtained without a prescription and relieve the pain and inflammation. Once the pain decreases, exercises of the affected area can begin. If the nearby muscles have become weak because of the disease or prolonged immobility, then exercises to build strength and improve movement are best. A doctor or physical therapist can prescribe an effective regimen. If the bursitis is related to an inflammatory condition like arthritis or gout, then management of that disease is needed to control the bursitis. When bursitis does not respond to conservative treatment, an injection into the joint of a long-acting corticosteroid preparation, like prednisone, can bring immediate and lasting relief. A corticosteroid is a hormonal substance that is the most effective drug for reducing inflammation. The drug is mixed with a local anesthetic and works on the joint within five minutes. Usually one injection is all that is needed.
Prevention
After taking a history and performing a physical examination, your physician may order x-rays to rule out other disorders. Your doctor may administer injections of corticosteroids and a local anesthetic to reduce swelling and ease pain. Also, to reduce swelling, your physician may draw excess fluid from the bursa with a syringe and then tightly wrap and compress the joint with an elastic bandage. In severe, persistent cases surgery to remove the bursa may be necessary. For infectious bursitis, antibiotics will be prescribed.
Hammertoe
 Overview
Overview
Hammertoes usually start out as mild deformities and get progressively worse over time. In Hammer toes the earlier stages, hammertoes are flexible and the symptoms can often be managed with changes in shoe styles and foot care products. But if left untreated, hammertoes can become more rigid and painful. Corns are more likely to develop as time goes on-and corns never really go away, even after trimming. In more severe cases of Hammer toes, corn lesions may evolve into severe ulcerations. These lesions frequently occur in patients who have vascular disease or are Diabetic with neuropathy. The ulcerations can extend to the bone and result in infection and possible loss of digit or amputation.
Causes
A common cause of hammer toe is wearing shoes that do not fit properly. Poorly-fitting shoes can hold the toes in an abnormal position and result in tightening of the muscles required to maintain that position. In particular, shoes that have high heels and are narrow at front tend to push the toes into an abnormal, bent position. Less commonly, diseases of the nerves, muscles, or joints (such as arthritis) can result in the hammer toe deformity.
 Symptoms
Symptoms
If the toes remain in the hammertoe position for long periods, the tendons on the top of the foot will tighten over time because they are not stretched to their full length. Eventually, the tendons shorten enough that the toe stays bent, even when shoes are not being worn. The symptoms of hammertoe include a curling toe, pain or discomfort in the toes and ball of the foot or the front of the leg, especially when toes are stretched downward, thickening of the skin above or below the affected toe with the formation of corns or calluses, difficulty finding shoes that fit well. In its early stages, hammertoe is not obvious. Frequently, hammertoe does not cause any symptoms except for the claw-like toe shape.
Diagnosis
A hammertoe is usually diagnosed with a physical inspection of your toe. Imaging tests, such as X-rays, may be ordered if you have had a bone, muscle, or ligament injury in your toe.
Non Surgical Treatment
Treating hammertoe involves straightening the toe, making tendons in the toes flexible again, and preventing the problem from returning. Some simple treatments include Soaking your feet every day in warm water, then stretching your toes and ankles by pointing your toes. Using over-the-counter pads, cushions or straps to decrease discomfort. Splinting the toe to keep it straight and to stretch the tendons of the foot. Exercising the toes to relax the foot tendons (a session with a physical therapist may help you get started with foot exercises). One simple exercise is to place a small towel on the floor and then pick it up using only your toes. You also can grasp at carpet with your toes or curl your toes up and down repeatedly. Wearing shoes that fit properly and give toes plenty of room to stretch out.
Surgical Treatment
Probably the most frequent procedure performed is one called a Post or an Arthroplasty. In this case a small piece of bone is removed from the joint to straighten the toe. The toe is shortened somewhat, but there is still motion within the toe post-operatively. In other cases, an Arthrodesis is performed. This involves fusing the abnormally-contracted joint. The Taylor procedure fuses only the first joint in the toe, whereas the Lambrinudi procedure fuses both joints within the toe. Toes which have had these procedures are usually perfectly straight, but they take longer to heal and don't bend afterwards. A Hibbs procedure is a transfer of the toe's long extensor tendon to the top of the metatarsal bone. The idea of this procedure is to remove the deforming cause of the hammertoes (in this case, extensor substitution), but to preserve the tendon's function in dorsifexing the foot by reattaching it to the metatarsals. Fortunately, the Gotch (or Gotch and Kreuz) procedure--the removal of the base of the toe where it attaches to the foot, is done less frequently than in years past. The problem with this procedure is that it doesn't address the problem at the level of the deformity, and it causes the toe to become destabilized, often resulting in a toe that has contracted up and back onto the top of the foot. You can even have an Implant Arthroplasty procedure, where a small, false joint is inserted into place. There are several other procedures, as well.
Bunions All You Need To Know
Overview
 In constrictive shoes, the big toe is forced to bend toward the second toe and the first joint of the big toe is moved out of place. To compensate for the realignment, the outside of the joint is increased in size. Tendons then begin to pull the toe into an abnormal position. Over time the change in position becomes painful and permanent. The change in position also causes the mechanics of the toes and foot to be affected. The joint at the base of the big toe carries a lot of weight when walking or running. In a normally shaped foot the position of the big toe helps create a wide base of support and stability. A foot that has had the big toe bent toward the second toe will tend to roll inward. This abnormal pronation, along with the ill-fitting shoes will make the Bunion even worse. If a person has a foot anatomy that is prone to Bunions, wearing footwear with a too-narrow toe box will accelerate the development of a Bunion. Wearing footwear with a wide toe box may help prevent or at least delay the development of Bunions.
In constrictive shoes, the big toe is forced to bend toward the second toe and the first joint of the big toe is moved out of place. To compensate for the realignment, the outside of the joint is increased in size. Tendons then begin to pull the toe into an abnormal position. Over time the change in position becomes painful and permanent. The change in position also causes the mechanics of the toes and foot to be affected. The joint at the base of the big toe carries a lot of weight when walking or running. In a normally shaped foot the position of the big toe helps create a wide base of support and stability. A foot that has had the big toe bent toward the second toe will tend to roll inward. This abnormal pronation, along with the ill-fitting shoes will make the Bunion even worse. If a person has a foot anatomy that is prone to Bunions, wearing footwear with a too-narrow toe box will accelerate the development of a Bunion. Wearing footwear with a wide toe box may help prevent or at least delay the development of Bunions.
Causes
Bunions develop when the pressures of bearing and shifting your weight fall unevenly on the joints and tendons in your feet. This imbalance in pressure makes your big toe joint unstable, eventually molding the parts of the joint into a hard knob that juts out beyond the normal shape of your foot. Experts disagree on whether tight, high-heeled or too-narrow shoes cause bunions or whether footwear simply contributes to bunion development. Other causes include inherited foot type, foot injuries, deformities present at birth (congenital). Bunions may be associated with certain types of arthritis, particularly inflammatory types, such as rheumatoid arthritis. An occupation that puts extra stress on your feet or one that requires you to wear pointed shoes also can be a cause.
Symptoms
The most common symptoms associated with this condition are pain on the side of the foot. Shoes will typically aggravate bunions. Stiff leather shoes or shoes with a tapered toe box are the prime offenders. This is why bunion pain is most common in women whose shoes have a pointed toe box. The bunion site will often be slightly swollen and red from the constant rubbing and irritation of a shoe. Occasionally, corns can develop between the 1st and 2nd toe from the pressure the toes rubbing against each other. On rare occasions, the joint itself can be acutely inflamed from the development of a sac of fluid over the bunion called a bursa. This is designed to protect and cushion the bone. However, it can become acutely inflamed, a condition referred to as bursitis.
Diagnosis
Your doctor can identify a bunion by examining your foot. Watching your big toe as you move it up and down will help your doctor determine if your range of motion is limited. Your doctor will also look for redness or swelling. After the physical exam, an X-ray of your foot can help your doctor identify the cause of the bunion and rate its severity.
Non Surgical Treatment
A bunion treatment must address the underlying cause of the deformity, not just the bump (bunion) itself but also the functions of the foot. The up and down motion of the longitudinal arches in the foot. The sideways motion of the transverse arch. Bunion aids effectively treat this underlying foot function while straightening the big toe because the mid-foot strap stabilizes the longitudinal arches and transverse arch. The toe strap gradually and gently pulls the big toe away from the second toe. The metatarsal pad helps align the transverse arch. The hinged splint enables the big toe to flex while walking and adapts to the contour of the foot, especially around the inflamed area of the joint. 
Surgical Treatment
A bunion is considered moderate when it pushes against the second toe. In fact, over time, the big toe can force itself under the second toe, causing it to buckle and form a "hammer toe." If non-invasive treatment is not effective, and the joint is still causing discomfort, the doctor may suggest a bunionectomy to realign the big toe. With this procedure, the bunion head is moved over realigning the angled great toe joint back to a normal position. The tendons and ligaments are also balanced for a more normal pull on the toe. In moderate bunion cases, you will experience a relatively rapid recovery. The procedure allows for immediate weight on the foot in a boot and return to tennis shoes in about a month. The choice of procedure best for each patient depends on the deformity size, the stiffness of the 1st metatarsal and the ease of realignment of the 1st metatarsal during the clinical exam.
Prevention
Make better shoe choices. If you?re a woman, avoid high-heeled footwear whenever possible (at the very least, choose shoes with heels lower than two inches), and make sure all your footwear has a wide, deep toe box. Whether man or woman, if you?re trying on shoes and your toes feel ?squished? or crowded by a particular shoe, reject that style and try another, or go for a larger size. You don?t need to invite trouble. In general, shoes that come to a point at the toe are bad news, as they tend to push the toes together into an overlapping pattern. Shoes with rocker soles will unload pressure on the bunion area. Examine your feet regularly. Note any redness, swelling or discoloration. Flex your toes and check for any stiffness. If there is any, think back to what you?ve worn or done in the past few days. If the condition persists more than a few days, or worsens, a visit to the podiatric physician is in order.
Overpronation Of The Feet Discomfort
Pronation is a turning outward of the foot at the ankle, which allows the foot to flatten. The pronation helps to absorb some of the compressive shock forces, torque conversion, adjustment to uneven ground contours, and maintenance of balance. It is necessary to have a certain amount of pronation to disseminate the energy of the foot-strike. If there is too little or too much pronation injuries may occur. When a foot and ankle pronates to a great degree, we call it over-pronation. Normally you can see the Achilles Tendon run straight down the leg into the heel. If the foot is over-pronated, the tendon will run straight down the leg, but when it lies on the heel it will twist outward. This makes the inner ankle bone much more prominent than the outer ankle bone.
Causes
Generally fallen arches are a condition inherited from one or both parents. In addition, age, obesity, and pregnancy cause our arches to collapse. Being in a job that requires long hours of standing and/or walking (e.g. teaching, retail, hospitality, building etc) contributes to this condition, especially when standing on hard surfaces like concrete floors. Last, but not least unsupportive footwear makes our feet roll in more than they should.
Symptoms
Over-pronation is a condition where the arch flattens out which makes the feet roll inward while walking. This condition is also known as flat feet. It imposes extreme additional stresses on the plantar fascia, a fibrous band of tissue which connects the heel to the forefoot. Over-pronation makes walking a painful experience because of the additional strain on the calves, heel and/or back. Treatment for over-pronation involves the use of specially-made orthotics which offers arch support and medial rear foot posting as corrective measures.
Diagnosis
Bunions, calluses and crooked toes may indicate alignment problems. So, it is important to ascertain the condition of a client's toes. Check the big toe to determine if the first joint of the toe is swollen, has a callus or bunion, and/or looks as though it abducts (i.e., hallux valgus) rather than pointing straight ahead. Also, look to see if the lesser toes seem to "curl up" (i.e., the person has hammer or claw toes). This may be indicative of damage to, or inflexibility of the plantar fascia caused by excessive flattening of the foot.
Non Surgical Treatment
Pronation and supination are bio-mechanical problems, and are best treated and prevented with orthotic inserts. But before you run out to buy orthotics it makes sense to get the right advice on footwear, and the best advice I can give you, is to go and see a qualified podiatrist for a complete foot-strike and running gait analysis. They will be able to tell you if there are any concerns regarding the way your running gait is functioning. After your running gait has been analysed, have your podiatrist, or competent sports footwear sales person recommend a number of shoes that suit your requirements. Good quality footwear will go a long way in helping to prevent pronation and supination. And, if needed, invest in a pair of orthotic inserts to further prevent excessive pronation or supination.
Prevention
Many of the prevention methods for overpronation orthotics, for example, can be used interchangeably with treatment methods. If the overpronation is severe, you should seek medical attention from a podiatrist who can cast you for custom-made orthotics. Custom-made orthotics are more expensive, but they last longer and provide support, stability, and balance for the entire foot. You can also talk with a shoe specialist about running shoes that offer extra medial support and firm heel counters. Proper shoes can improve symptoms quickly and prevent them from recurring. Surgery can sometimes help cure and prevent this problem if you suffer from inherited or acquired pes planus deformity. Surgery typically involves stabilizing the bones to improve the foot?s support and function.
Physiotherapy For Severs Disease
Sever's disease or Calcaneal apophysitis is a condition that affects children between the ages of 10 and 13 years. It is characterized by pain in one or both heels with walking. During this phase of life, growth of the bone is taking place at a faster rate than the tendons. Hence there is a relative shortening of the heel-cord compared to the leg bones. As a result, the tension the heel-cord applies to the heel bone at its insertion is very great. Moreover, the heel cord is attached to a portion of the calcaneus (heel bone) that is still immature, consisting of a mixture of bone and growing cartilage, called the calcaneal apophysis, which is prone to injury. Compounding to this is the fact that all these changes are happening in a very active child, prone to overuse. The end result is therefore an overuse syndrome of injury and inflammation at the heel where the heel cord (Achilles Tendonitis) inserts into the heel bone (Calcaneal apophysitis).
Causes
The actual pathology of the condition is one of more of an overuse syndrome in which the growth plate of the heel may become slightly displaced, causing pain. Biopsies of similar conditions have shown changes consistent with separation of the cartilage. The cause of Sever's disease is not entirely clear. It is most likely due to overuse or repeated minor trauma that happens in a lot of sporting activities - the cartilage join between the two parts of the bone can not take all the shear stress of the activities. Some children seem to be just more prone to it for an unknown reason, combine this with sport, especially if its on a hard surface and the risk of getting it increases. A pronated foot and tight calf muscles are common contributing factors. The condition is very similar to Osgood-Schlatters Disease which occurs at the knee.
Symptoms
The main symptom of sever's disease is pain and tenderness at the back of the heel which is made worse with physical activity. Tenderness will be felt especially if you press in or give the back of the heel a squeeze from the sides. There may be a lump over the painful area. Another sign is tight calf muscles resulting with reduced range of motion at the ankle. Pain may go away after a period of rest from sporting activities only to return when the young person goes back to training.
Diagnosis
Sever's disease is diagnosed based on a doctor?s physical examination of the lower leg, ankle, and foot. If the diagnosis is in question, the doctor may order X-rays or an MRI to determine if there are other injuries that may be causing the heel pain.
Non Surgical Treatment
First, your child should cut down or stop any activity that causes heel pain. Apply ice to the injured heel for 20 minutes 3 times a day. If your child has a high arch, flat feet or bowed legs, your doctor may recommend orthotics, arch supports or heel cups. Your child should never go barefoot. If your child has severe heel pain, medicines such as acetaminophen (one brand name: Tylenol) or ibuprofen (some brand names. Advil, Motrin, Nuprin) may help.
Recovery
In some cases, children will simply outgrow Sever's Disease when they reach a certain age, but this does not mean that symptoms should be ignored. If children express that they are in pain, this should always be taken seriously by their parents or guardians. Heel pain may be a sign of Sever's Disease and this condition should not be left untreated, due to the damage it can cause to the growing heel bones. Scheduling a doctor's appointment is always the first step to take in gaining a diagnosis of symptoms and speedy help for the child.
Acquired Flat Foot Tibialis Posterior Muscle
Overview
Adult acquired flatfoot deformity (AAFD), embraces a wide spectrum of deformities. AAFD is a complex pathology consisting both of posterior tibial tendon insufficiency and failure of the capsular and ligamentous structures of the foot. Each patient presents with characteristic deformities across the involved joints, requiring individualized treatment. Early stages may respond well to aggressive conservative management, yet more severe AAFD necessitates prompt surgical therapy to halt the progression of the disease to stages requiring more complex procedures. We present the most current diagnostic and therapeutic approaches to AAFD, based on the most pertinent literature and our own experience and investigations. 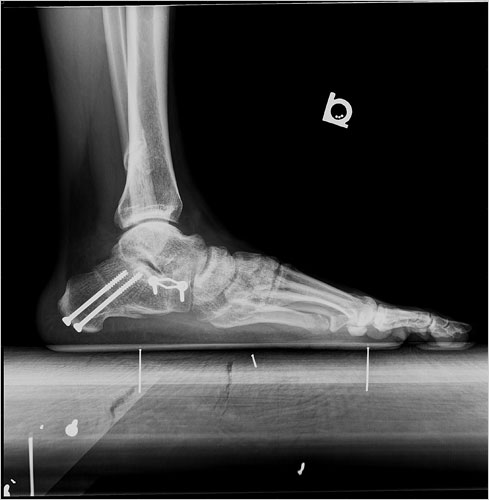
Causes
There are numerous causes of acquired adult flatfoot, including fracture or dislocation, tendon laceration, tarsal coalition, arthritis, neuroarthropathy, neurologic weakness, and iatrogenic causes. The most common cause of acquired adult flatfoot is posterior tibial tendon dysfunction.
Symptoms
As different types of flatfoot have different causes, the associated symptoms can be different for different people. Some generalized symptoms are listed. Pain along the course of the posterior tibial tendon which lies on the inside of the foot and ankle. This can be associated with swelling on the inside of the ankle. Pain that is worse with activity. High intensity or impact activities, such as running and jumping, can be very difficult. Some patients can have difficulty walking or even standing for long periods of time and may experience pain at the inside of the ankle and in the arch of the foot. Feeling like one is ?dragging their foot.? When the foot collapses, the heel bone may shift position and put pressure on the outside ankle bone (fibula). This can cause pain in the bones and tendons in the outside of the ankle joint. Patients with an old injury or arthritis in the middle of the foot can have painful, bony bumps on the top and inside of the foot. These make shoe wear very difficult. Sometimes, the bony spurs are so large that they pinch the nerves which can result in numbness and tingling on the top of the foot and into the toes. Diabetic patients may not experience pain if they have damage to their nerves. They may only notice swelling or a large bump on the bottom of the foot. The large bump can cause skin problems and an ulcer (a sore that does not heal) may develop if proper diabetic shoe wear is not used.
Diagnosis
There are four stages of adult-acquired flatfoot deformity (AAFD). The severity of the deformity determines your stage. For example, Stage I means there is a flatfoot position but without deformity. Pain and swelling from tendinitis is common in this stage. Stage II there is a change in the foot alignment. This means a deformity is starting to develop. The physician can still move the bones back into place manually (passively). Stage III adult-acquired flatfoot deformity (AAFD) tells us there is a fixed deformity. This means the ankle is stiff or rigid and doesn???t move beyond a neutral (midline) position. Stage IV is characterized by deformity in the foot and the ankle. The deformity may be flexible or fixed. The joints often show signs of degenerative joint disease (arthritis).
Non surgical Treatment
Initial treatment is based on the degree of deformity and flexibility at initial presentation. Conservative treatment includes orthotics or ankle foot orthoses (AFO) to support the posterior tibial tendon (PT) and the longitudinal arch, anti-inflammatories to help reduce pain and inflammation, activity modification which may include immobilization of the foot and physical therapy to help strengthen and rehabilitate the tendon. 
Surgical Treatment
Surgical intervention for adult acquired flatfoot is appropriate when there is pain and swelling, and the patient notices that one foot looks different than the other because the arch is collapsing. As many as three in four adults with flat feet eventually need surgery, and it?s better to have the joint preservation procedure done before your arch totally collapses. In most cases, early and appropriate surgical treatment is successful in stabilizing the condition.